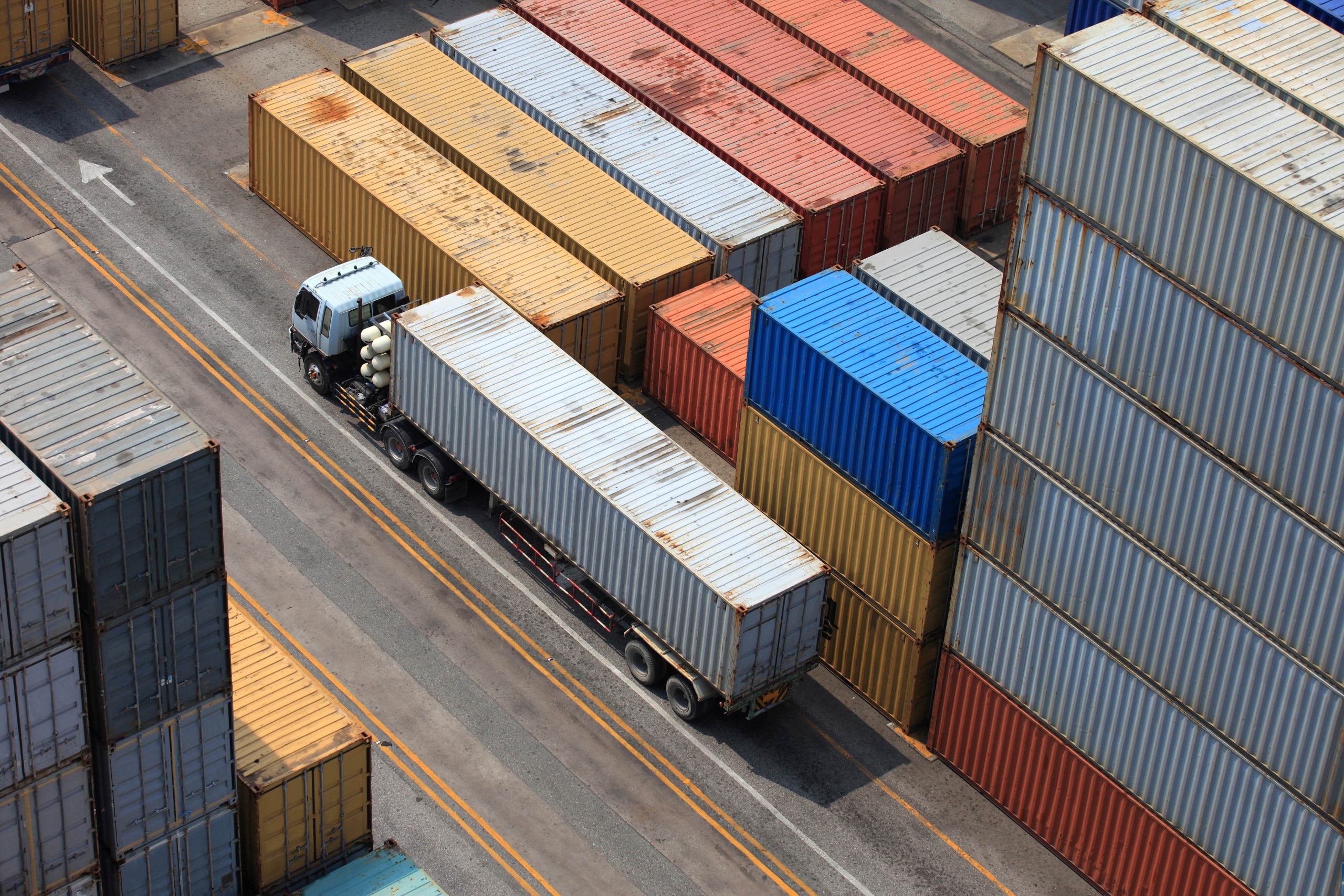
Topic of today is Difference between Intramodal and Intermodal Transportation. “Intermodal” refers to transporting significant freight shipments from one location to another. And you can perform this by utilizing more than one mode of transportation.
Intermodal transportation containers are large and standard shipping containers. They are designed and built to transport goods from one mode of transportation to another. This can be from a boat to a train to a truck, without the need to unload and reload their cargo. Intermodal containers are also known as multimodal containers.
In this guide, at the end, we will also discuss about difference between Intramodal and Intermodal transportation.
Intramodal and Intermodal Transportation | What are the features of Intermodal containers?
- Possibly, you will use a different transporter at each stage of the cargo. This is why you will pay less for care and be able to take advantage of lower rates. This will save you money.
- The effects on the environment are minimal. You can select options that are friendly to the environment. This is possible when you use modes of transportation that serve many purposes.
- It benefits in terms of quality, limits, and security that do not fluctuate. Transporters have easier access to more types of gear, and their itineraries tend to be more consistent. You can establish connections with them and make it simpler for them to collaborate.
What exactly are some of the uses for intermodal containers?
The majority of people are aware that the following can be transported via intermodal containers:
- Products that can withstand a great deal of use and abuse
- Freight that must be maintained at a temperature below freezing or below room temperature. This can be fish, meat, plants, and medications.
- Coffee and cocoa are two examples of loads that are difficult to decompose, but that can face damage by accumulation.
- Larger-than-usual shipments, such as those consisting of lumber, large tools, and building supplies
- Large quantities of synthetic materials, oils, fluids, and food goods are stored in tank compartments. Some of these materials are hazardous, while others are not.
In what sizes are they available?
There are two primary categories of storage containers, both of which have more than one application:
1. TEU stands for “Twenty-foot-Equivalent Unit
Its holder measures 20 feet in length, 8 feet in width, and 8 feet in height. Its abbreviation is a twenty-foot identical unit (TEU). Between 9 and 11 beds can fit inside a TEU. But this number varies depending on whether the beds are regular beds or EUR beds.
- Lengthwise: 19 feet and 3 inches
- 7 feet and 8 inches in width
- The height is 7 feet, 9 inches, and 7/8 of an inch.
- The width of the door opening is 7 feet and 8 inches. And the height is 7 feet and 5 inches.
- There are 1,165 feet cubic in total volume.
- One unit of measurement is equivalent to forty feet.
2. FEU stands for “Forty-Foot Identical Unit.”
It’s a holder that you can use for various purposes. Its abbreviation is a forty-foot identical unit (FEU). It measures around 40 feet in length, 8 feet in width, and 8 feet in height. The number of beds that can fit inside an FEU ranges from 20 to 24. And this is determined by whether the beds are normal beds or EUR beds.
- 40 foot
- 39 feet 5 inches in length total.
- 7 feet and 8 inches in width
- The height is 7 feet, 9 inches, and 7/8 of an inch.
- The width of the door opening is 7 feet and 8 inches. And the height is 7 feet and 5 inches.
- Size in cubic feet: 2,350 cu. Ft.
Learn all about Intermodal Containers – Working Procedure
What is the difference between intramodal and intermodal transportation?
Now let’s talk about difference between Intramodal and Intermodal transportation!
The number of ways passengers can go from one location to another is extremely important. This is the primary criterion that differentiates multi-purpose transportation from intramodal transport transit. The prefix “inter” indicates that it can be available in more than one location. But the prefix “intra” indicates that it is located within something.
Nevertheless, modes of transportation for more than one thing will employ at least two modes of shipment. This is vital for transporting both people and goods. To transport new products, utilizing a multi-purpose system involves air transport and road transport.
On the other hand, an intramodal system uses only one mode of transportation. This can include large trucks and smaller trucks. Hence, this ensures that deliveries take place in the appropriate order.
The multi-purpose transportation system has gained more popularity. This happens when the business sector has placed a greater emphasis on increasing productivity. And this was to reduce expenses and make prices more competitive.
This is because it provides carriers and transporters with various benefits. This can include time, speed, adaptability, and reliability that assist them in meeting the market’s requirements. Because of technological advancements make multi-purpose systems for transporting loads and shipments a lot more enticing to consumers.
For instance, cranes are accessible with a Global Positioning System (GPS). They help to locate their destinations to stay a lot more desirable.
Read More:
Intermodal transportation vs Multimodal Transportation
Characteristics of Intermodal Transportation, How It May Affect Freight Industry And Its Future
Examples of Intermodal Transportation, How they work and their Impacts