What Is Intermodal Shipping?
Businesses trying to cut costs on freight shipping are increasingly turning to intermodal shipping as an option. Using two or more different means of transportation to move freight is known as intermodal shipping. Cargo can be loaded into these containers, enabling seamless transportation between trucks, trains, and cargo ships.
This technique of transportation got first used in Britain in the eighteenth century. The British utilized it to transport containerized coal through their network of canals. However, intermodal became the favored method for marine shipping in the 1960s.
Intermodal Strategy:
It is a strategy that logistics firms and international organizations use to combine various modes of transportation. Later, by facilitating simple handling between modal systems, containerization and standardized international container sizes increased the profitability of intermodal transport.
Intermodal transport currently dominates the world’s logistics and supply chain. Therefore, it’s crucial for everybody working in the logistics industry to comprehend this idea that underpins the global shipping and trucking sectors. This post will look at intermodal transportation’s characteristics, advantages, and market environment.
Intermodal Freight Brokers
To expedite the movement of goods from one site to another, intermodal freight brokers are people or businesses who collaborate with importers, freight carriers, or consignees. The completion of logistics operations between several modes of transportation, such as sea, train, and air, is the responsibility of an intermodal broker. Intermodal brokers ensure that shipments are timely and according to schedule, which ultimately contributes to the success of a supply chain.
These brokers are crucial in linking the intermodal logistics sector. And if you, as a shipper, want to handle your shipping operations without any obstacles or want to stop taking large shipments, it is a good idea to incorporate them into your firm. You can focus on growing your business while they handle your intermodal logistics and total shipping.
Intermodal freight transportation combines two or more different means of shipping, such as trucking, rail transport, shipping, or aviation, to carry cargo to its destination. Each carrier is in charge of a particular intermodal logistics and transportation model. As a result, intermodal shipping involves several freight invoices from various airlines.
Learn all about: Challenges Faced by Air Cargo Industry
Intermodal Container – Working Procedure
A blank truck pulls up at the consignee site to begin the intermodal shipping procedure. A container at the back of the truck is loaded with the goods by the shipper or transporter in charge. From this moment until they get to their destination, probably no one will handle these items. The vehicle moves to a train yard through the road system. The logistics business uses a railway to transport the containers here. The container may get transferred by train to a port for shipping or to a rail station in the chosen location.
The shipping business transports these containers to the final port via the maritime system. The container gets unloaded, then moved to another vehicle. A different train may also get used to convey it further inland before being placed on a truck. The container might get delivered by this truck to the final modal station. Only specific businesses offer the service of drayage, the vehicle used to transport these commodities.
What Comes Next?
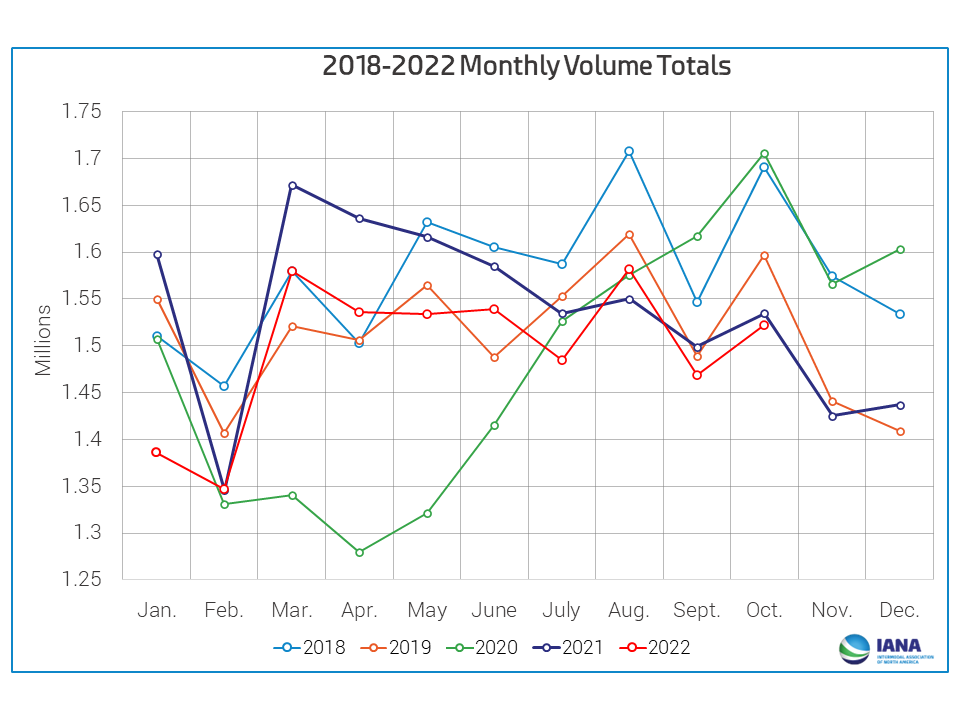
What comes next? The products are now taken out of the container by the logistics company. The container is currently vacant and prepared for a fresh load. The logistics company also handles the final mile of delivery to the customer. This shipping method has tremendous benefits. Here is a chart showing Monthly Volume Totals from 2018 to 2022.
Why do businesses employ this transportation? It enables a logistics business to use each mode of transportation’s capabilities. For interior transit, rail service is frequently less expensive. Long-distance international travel can get accelerated by shipping. Additionally, vehicles are necessary for the final mile of local deliveries and pickups.
Learn all about: Characteristics of Intermodal Transportation, How It May Affect Freight Industry And Its Future
Benefits of Intermodal Shipping
Because it provides so many advantages, this transport method has evolved into the foundation of the trade and logistics sectors. The following are some of the primary benefits of intermodal transportation for your company:
Lower Prices
By transporting freight in intermodal containers, businesses can cut their transportation costs. Significant fuel savings get achieved by using rail and trucks. Trucks use a lot more diesel than trains do. A train can travel nearly 450 miles with a ton of freight on a single gallon of fuel. Long-distance trucks can result in significant fuel costs, although trains can mitigate this effect. Additionally, businesses will lessen their carbon footprint. The capacity to ship in containers is among the intermodal transportation benefits that reduces costs.
Containers handling occurs together. It lowers the cost of transportation because switching a shipment from a truck to a train, ship, or any other arrangement only requires minimal work. Containers are simple to swap between and will fit into any mode, improving the carrier process’s effectiveness.
Standard Capacity
Trucks and intermodal rail mobility, in particular, provide dependable capacity. Less competition makes it easier to procure freight for intermodal transport, reducing costs even further and giving capability when and where it is required. This way of transport is growing in popularity with shippers due to the shortage of operators and higher transportation traffic.
Companies can transport via intermodal at any time and a competitive price, as opposed to paying excessive rates to ensure capacity or turning over backward to facilitate carriers. It is an effective strategy to deal with the present issues facing the trucking sector, as carriers are raising prices and sluggishly providing service.
Premium Service
The level of service is arguably the most significant advantage of adopting multimodal transportation. In comparison to other modes, intermodal is more inventive. Due to increased train speeds and shorter car turnaround times, shippers have found that intermodal transit is quicker than OTR.
Safety
Additionally, intermodal delivery can increase cargo security and safety. Since trains travel on a fixed track, they are less likely to be present in an accident when transporting dangerous or highly flammable cargo. Less worry of the loading, unloading, and carrying hazardous commodities results in quicker transportation.
The doors on a train cannot get opened when containers fall into the well, and when they are double-stacked, the uppermost container is 15 feet off the ground and challenging to access. Additionally, the yard sees fewer cars, which keeps the freight moving.
Convenience
It is also practical to use this transportation. In addition to having capacity when required and saving shippers 10 to 30 percent over trucking, intermodal shipping is now just as reliable and efficient as OTR shipping owing to industry-wide technical advancements.
Shippers no longer have a 3-day delivery window and are present in the dark while they wait and hope their shipment arrives. The exact shipping OTR transparency into shipment status is available, simplifying the choosing of an intermodal service and improving the accuracy of mode comparisons.
Learn all about: Intermodal Transportation Advantages and Disadvantages
Intermodal Calculator
Are you looking for a comparison of OTR transit? Do you want to understand how intermodal shipping can help you cut back on carbon emissions? For all the solutions, utilize the intermodal savings calculator.
- Enter your starting point and ending point into this calculator to:
- View the shipping route for your package.
- Compare the transit times for intermodal and OTR.
- Find out how much you can save by shipping intermodally.
- Chart your annual reductions in carbon emissions.
- Using the Intermodal Savings Calculator, you may choose the best method of transportation for your requirements.
What Products Can You Ship Using Intermodal?
Almost everything that can fit in an intermodal container can get shipped via intermodal transportation. It could be any commodity as long as it does with what the railroad is prepared to move. It gets used to transport tyres, consumer products, and even diapers. The fact that this transportation method is such a flexible capacity source makes it valuable.
Intermodal containers can carry a wide range of goods since freight railways frequently convey more than just goods; they also often ship people, dogs, and other living things.
Does Intermodal Provide Shipment Visibility 2022?
Shippers may become anxious about losing sight of their inventory while goods transportation occurs by trucks and railroads. Although historically, that may have been the case, now intermodal shipping provides the visibility shippers seek. Therefore, the phrase “loss of visibility” has become misinterpreted. Most clients anticipate being able to access that visibility. This shipping aims to offer a smooth, end-to-end solution to clients.
All of the company’s containers have satellite tracking installed to improve cargo visibility, along with artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, enabling them to inform a customer at any time of where their container is and when it will arrive at its destination. Then some processes allow clients to obtain pricing, receive push notifications, proactively monitor and trace shipments, and generally have the end-to-end visibility they require.
What is An Example of Intermodal Transportation?
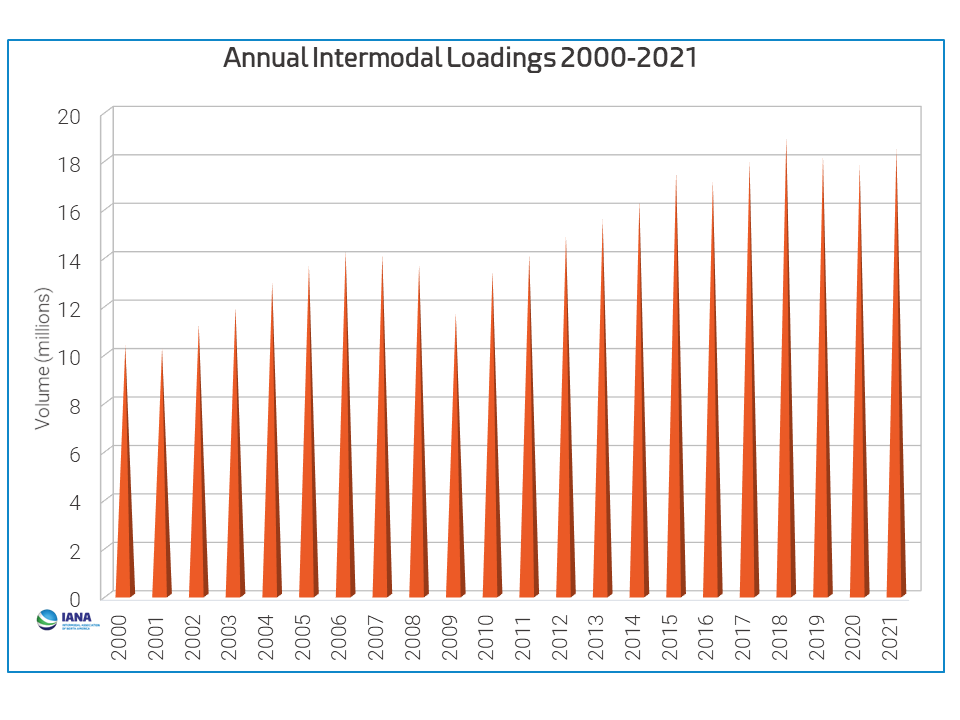
The popularity of multimodal transportation has changed how businesses deliver goods and services. It improves logistics efficiency while easing traffic and reducing carbon emissions. Here is a chart showing the Annual Intermodal Loadings from 2000 to 2021.
The intermodal industry will rise by 20% in the following five years. By 2030, it may rank among the top three worldwide sectors.
One method is to utilize autonomous vehicles created with efficiency and safety in mind. Trucks replacement by autonomous vehicles capable of traveling vast distances at incredible velocities will occur without halting or slowing down short freight. Some examples of Intermodal Transportation are:
THE FERRY SERVICE
An illustration of multimodal transportation is the ferry service. It is a form of transportation that uses a boat to go over water and land. This mode of transport has been in use for many years and is still widely utilized today. The ferry service is one kind of multimodal transportation. Various transportation methods can reach it, including buses, vehicles, trains, and airplanes. In times of conflict or natural disaster, ferries are present to swiftly and safely transport people between islands or continents.
TRAIN SERVICE
One instance of multimodal transportation is the railway service. It is an excellent illustration of how several modes of transportation are present in combination. This transportation method integrates two or more modes of transport to offer a better traveling experience. You could take a bus that connects two cities and then a train to get from one to the other.
BUS SERVICE
You can use the bus system as one of the illustrations of multimodal transportation. In locations without rail or subway stations, it is a system that offers bus transportation. Moving the buses from one method of transportation to another is necessary.
Buses are present as public transportation in numerous cities. They board them on the sidewalks, airports, bus stations, or curbs.
RAILROADS
One example of an intermodal mode of transportation is the railroad. They offer the most precise illustration of how technology may alter our lives. The railroad was present early in the 19th century and has been developing ever since. The railroad aided in the movement of commodities, people, and ideas over land and the ocean. With minimal effort from carriers, it can transport more cargo than any other kind.
Over 200 years of railroad existence have contributed to how we live today. In the past, railroads were a vital component of our society. Still, thanks to technological improvements, they are no less significant.
Learn all about: Examples of Intermodal Transportation, How they work and their Impacts
What is the First Step for Shipping Intermodal Freight?
If this method of transportation appeals to you, consider how it might change how you handle inventory. Businesses ensure that the facility-level staff knows the lead time chain because it is crucial to a successful transfer. It will be vital if the facility-level lead time is accurate.
Using a cost-benefit analysis, one can compare intermodal versus an over-the-road (OTR) truck solution. We advise considering the overall value, not just the inventory prices, compared to the truck. Consider the complete range of what you’re getting, including the consistency, the level of service, and, most likely, the price difference from a truck.
Use an intermodal savings calculator, which enables you to compare intermodal and OTR transit times, calculate intermodal shipping costs, and estimate annual carbon emission reductions as one easy step shippers can take.
What are the Latest Intermodal Shipping Trends 2022?
Greater shipment visibility and more reliable service are two intermodal trends that have evolved in recent years. So what comes next?
In the old days, the intermodal sector’s drayage side started its operations through independent contractors and third parties. Businesses are proactively trying to manage more of their drivers using their trucks. That’s a tendency that will persist. More control translates into even more reliable, punctual service.
Additionally, technological advancements are on the horizon, especially in the form of Application Programming interfaces (API). Businesses are pushing for greater technology integration and intermodal to dominate visibility and knowledge delivery to customers. They’re making significant investments in it, and based on how effective and superior it is to communicate information in real-time, this trend will continue.
Since there is a lot of data available and it can be overwhelming, the focus should be on data that significantly impact the customer’s business. APIs enable transportation companies to communicate information quickly between different technology platforms, so it will be crucial to comprehend what information customers want.
Hub Group Role in Intermodal Shipping
Hub Group has been a part of intermodal transportation since 1971. The company didn’t have any of its assets when it started its services; instead, it was a broker for what was then famous as a piggyback service, which involved loading flat cars with trailers of products. Since that time, a lot has changed. Currently, the business has 38,000 containers, and 4,000 drivers are present to pick up and transport freight.
They see their continued function as the link between customers and intermodal, offering the trucking options and capacity necessary to continue providing top-notch service.
They intend to keep focusing on locating chances for savings, efficiency, and visibility for their customers and supply chains. One option is intermodal transportation, which now offers cost- and fuel-effectiveness, high service levels, and environmental sustainability. Customers can still view this method of transportation as the excellent source of capacity that it is.
Intermodal vs Transloading
Intermodal Shipping
This type of shipping technically refers to the movement of cargo using two or more modes of transportation. However, when rail shippers use the term “intermodal,” they typically refer to loads that transit in containers among trucks and trains.
Intermodal transportation operates as follows:
- Merchandise gets within a container.
- A truck chassis is present to support the container.
- Container transportation occurs by vehicle to an intermodal ramp
- When the container reaches an intermodal ramp, it is present on a flat or well car to transport by train.
- After that, the container passes to a vehicle for the final delivery.
Transloading
In this, goods transportation occurs across buses and trains, and transloading is identical to intermodal transport. However, instead of traveling in a single container, goods are present between vehicles with transloading.
For example, a crane may raise heavy items like metal beams off a train and put them on a flatbed truck, or a forklift may transport palletized cargo from a pickup to a larger rail car.
Transloading operates as follows:
- The container’s transportation occurs by truck to a facility for transloading.
- Products are present onto rail cars at the transload facility.
- The product type dictates how it gets transported and what kind of rail car it goes on.
- Products are moved back to trucks if necessary for the final delivery.
Learn all about: Intermodal vs Transloading
Read More:
Intermodal transportation vs Multimodal Transportation
Difference between Intramodal and Intermodal Transportation
Ocean Freight Market Outlook 2022-2024
Air Cargo Statistics 2022 Analysis
Share to help other by using your favorite social media buttons below.